
Proliferation/acceleration of artificial intelligence as a result of COVID
Wendy Nguyen

introduction to the proliferation of artificial intelligence due to
covid-19
Machinery and artificial intelligence have been a normal part of the work field for a few decades. Over the years as technology advances, so does the technology in workplaces.
However, due to covid there is a higher demand for machines to completely replace many jobs which would usually be done by humans to try and limit the spread of the virus as much as possible. More machines are being developed at a faster rate to help adapt to the new lifestyle that COVID-19 has forced upon us with thousands of new inventions that have been rushed to be made as a response to the virus.
The use of machines was once seen as incredibly useful to humans but seeing how situations have changed over the past year, many people are scared of how the same machines that once helped them could now replace them. At a normal rate, the impact of artificial intelligence aiding or replacing human workers would not have a large effect on society as thousands of new job openings would appear at a similar rate. The problem starts when the rate of machines being introduced into the work field is much higher than the rate of new job openings. A drastic decrease in the employment rates also brings down many other aspects, an example being the GDP of a country.
Who are the winners and losers in relation to this issue?
Unlike most other global issues, the proliferation of artificial intelligence negatively impacts first world countries much more than third world countries. As the virus gets worse in many countries, the temporary demand to replace human workers is skyrocketing and may even become a long term solution if seen as more effective to society even after the pandemic is over.
The retail and customer service industries are some of the sectors that have been largely impacted by this pandemic but these losses are often short term as they make a recovery with the help of AI. In retail, the need for cashiers has already been slowly decreasing but with the hand for covid, there has been an even larger decline in a smaller time span as many stores now offer self serve checkouts. Self serve checkouts take up less space, cost less than hiring employee (long term) and have become more popular as limiting human interaction where possible is desired during a pandemic. Even after the pandemic ends, the use of self serve machines would still be popular which is why companies may benefit from this but employees will not. This is why employees are considered as the biggest 'losers' in this situation as the need for employees has decreased massively and companies have managed to find other ways around the problem. This not only impacts job availabilities currently but also in the long run as technology would only get more advanced and it would take multiple years for job openings to catch up with the use of robots in workplaces. The worse the pandemic gets, the number of robots replacing humans would increase with it as there would only be more deaths and people unable to work. Companies do not have extra money to waste especially during a recession which is why the longer the pandemic lasts, the more likely companies will opt to using AI.
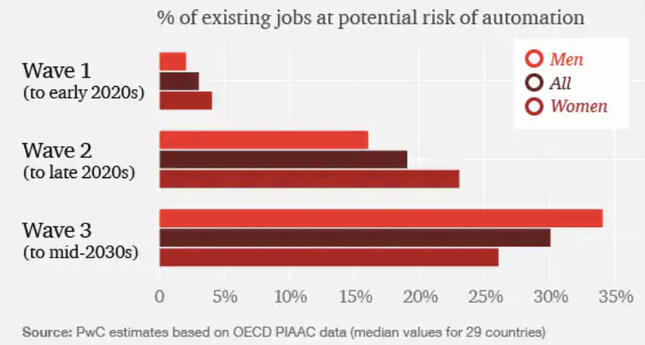
The overall economy of countries affected by COVID are predicted to have a large growth once the pandemic is over. As businesses have to understand how to work with the virus to not make a loss, the sudden increase of AI in the field helps with productivity in companies which makes it possible for cheaper and a larger amount of products to be produced and exported out. Without a situation like COVID, it would have taken much longer for businesses to use more robots as the sudden push without preparation caused an undesired situation - multiple setbacks in the industry. As shown in the graph below, 67% of companies started using more technology to help assist their business as a result of COVID. If done strategically, businesses would not be negatively impacted by the increase of robots at work at all.
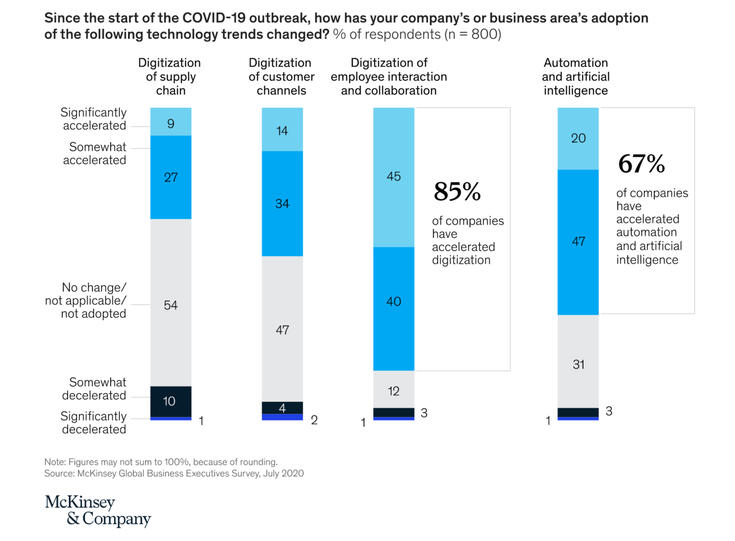
The technology sector would become much more popular as more jobs would be available due to the demand for maintenance that comes with the sudden increase of AI usage. Many technology brands also gain from the proliferation of AI as the majority have seen an increase in demand over the past year which for most is a positive but may also become negative if the demand is too high and the company is unable to keep up with it.
People in the medical field also benefit as there has been a shortage of medical professionals and having help in any possible way would help with the lack of assistance from humans. The suddenly increased usage of technology, in this case, would obviously be more advantageous than having little technology to assist them. The same would go for businesses that require physical assistance but can not meet the demand due to the risk of exposure to COVID via human interactions.
Explain why the issue has come about and how it has changed or evolved over time
Introducing artificial intelligence in work environment was seen as beneficial at first but since it has been forced to happen at a much quicker rater than what is natural from COVID, this situation has now evolved to become a problem for contemporary society. In the past, automation and job loss/lowered GDP have had very little correlation with each other. This issue is currently a big issue as unemployment rates are already incredibly high and having some robots on the field should allow for more people to work through this virus. However, since many of the machines used require minimum assistance or no assistance from humans, this makes it much harder for employment rates to go back to normal in this pandemic.
Economic implications, international trade to the proliferation of AI
As a result of the proliferation of artificial intelligence, the main economical implications of this issue would be a drop in GDP. As some of the main factors to calculating the GDP of a country is income and expenditure, the increased rates of unemployment would have a huge impact. Unemployment rates have been at their lowest in decades and having machines replacing thousands of workers does help with productivity but not the overall GDP of a country. With fewer people working, many would decrease the amount that they spend which would decrease the overall expenditure of the country. Though businesses and large companies may earn more money from using machinery over workers, giving already wealthy people even more money would spend would have little effect on the GDP as they already have their own money and would only spend a small portion of what they earn while people who have less money would use a larger percentage of their income.
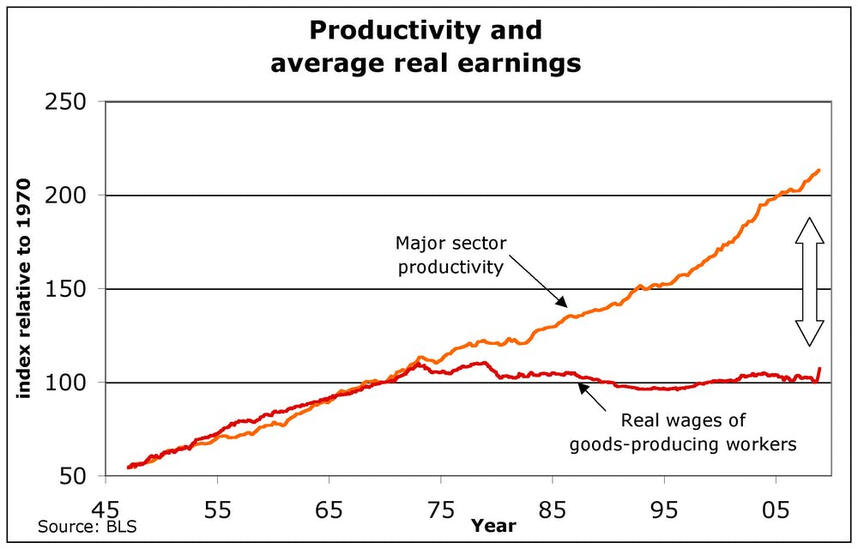
Another large factor that helps calculate the GDP of a country is production. The value of different sectors in production would increase due to more work force hours being put in which would help make more products at a cheaper cost. This would make it easier for a trade surplus to occur which does improve the economy. However, with more trade surpluses, it would be expected that more people are employed which is one of the reasons why it would improve the economy. In this case, however, robots, a one-off payment with maintenance fees, do not help with the income of the country and only one time for the expenditure. The GDP of the country would not grow much until employment rates manage to catch up with the number of jobs that have been replaced by AI. A trade surplus may also lead to higher interest rates but higher productivity would also make items more affordable. The graph below shows how productivity overall has greatly increased while the wage of the workers stay the same, in other words, how robots may help with production but not the wage and expenditure of people.
three suggested solutions to reduce the impacts of technology proliferation
To help reduce the sudden job losses that the rapid increase in AI has assisted with includes:
changing the education system focus more on analysing and creativity to better suit society in the future where robots are heavily involved in work fields and to catch up with the current gap in use with technology. This could also work on adults (reskilling employees) to adapt better to changes and normalise the use of technology.Opening up as many new jobs as possible. Many more engineering jobs will be needed and shifting the interest to jobs with high demand would help to even the job loss to jobs found ratio.increase country expenditure to stimulate a growing economy. This could be done by increasing certain taxes alongside additional income to people who live in the country to promote consumer spendings.
Research conducted by organisations
Not many organisations exist that focus on tackling the negative impacts of the proliferation of technology as most focus on job losses which is mainly caused by COVID and seen as a first world issue which is why this topic will be focusing on organisations that research technological unemployment and how to respond to it.
The Century Foundation is a "public policy think tank" research company based in New York that has looked into technological unemployment pre-covid and have a few articles written on how to respond to robots replacing workers. One of their articles mentions the TAA (trade adjustment assistance) which would help with job losses caused by AI and include some ways of how the TAA could improve their support. The trade adjustment assistance was made to help ease the damage that different sectors of the economy may take due to various reasons. In the conclusion of the article, the company mentions how it would be desired for robots to increase productivity while making new jobs for humans so that the two can work together for maximum productivity and economic growth. Another article by TCF also mentions changing the TAA in response to this situation, quoting "A logical place to start is by reforming Trade Adjustment Assistance into a more effective and powerful response to worker dislocation." (https://tcf.org/content/report/respond-job-losses-technology-trade-policy-choices/)
five actions that anyone can do to help
post on social mediaMany posts have been made with information on the topic to help spread awareness of the chosen situation. A similar one with unemployment rates, lower income and expenditure and the increased use of machinery that has taken over jobs can be put into the post. The people who use social media are the people who are able to make a change and this is a great way to share information around.
educate yourself about this situation and learn how to work around it. The possibility of certain jobs not existing in the future always exists and learning how to deal with this possibility by understanding how these machines may help us in the future once we understand how to work with them better. The goal is to have robots and human both support eachother.multiple streams of incomeUsing the proliferation of technology to your advantage by having multiple streams of income, some of which may be with the help of technology. With multiple streams of income, an issue like the proliferation of AI would impact you and the economy less as there is still steady money coming in. This could be through investing, an online business, tutoring online, etc...
supporting smaller businessesIf possible, purchasing from smaller, local businesses can help keep many jobs and also stimulate the economy even it if is by a fraction. This may not be possible for everyone as some people may not be able to afford to pay more especially with little income.
donating or volunteeringSimilar to the previous point, this may not be possible for everyone to do but helping others out when possible can mean a lot to people in need. This may not directly stimulate the economy as you would not get paid for these but allowing for others to save more money would mean that they would have more money to spend.
Gaskell, A., 2020. Automation, COVID, And The Future Of Work. [online] Forbes. Available at: <https://www.forbes.com/sites/adigaskell/2020/10/16/automation-covid-and-the-future-of-work/?sh=2cdbe9035e10> [Accessed 26 May 2021].reliability: 3.25/5 - not the most informative article, uses information from multiple sources.
Kelly, J., 2020. U.S. Lost Over 60 Million Jobs—Now Robots, Tech And Artificial Intelligence Will Take Millions More. [online] Forbes. Available at: <https://www.forbes.com/sites/jackkelly/2020/10/27/us-lost-over-60-million-jobs-now-robots-tech-and-artificial-intelligence-will-take-millions-more/?sh=5c3189511a52> [Accessed 27 May 2021].reliability: 3.5/5 - large brand, has quite a number of quotes from interviews which may not be the most honest, experienced author.
Lund, S., Cheng, W., Dua, A., Smet, A., Robinson, O. and Sanghvi, S., 2020. What 800 executives envision for the post pandemic workforce. [online] Available at: <https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/future-of-work/what-800-executives-envision-for-the-postpandemic-workforce> [Accessed 27 May 2021].reliability: 3.5/5 statistics are based on certain companies that they decided to survey (possibly skewed as companies could be high end or all clothing), brand is a worldwide managing firm.
Meyer, H., 2019. Five policies to deal with the loss of jobs to automation (UBI is not one of them). [online] LSE Business Review. Available at: <https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/businessreview/2019/04/12/five-policies-to-deal-with-the-loss-of-jobs-to-automation-ubi-is-not-one-of-them/> [Accessed 25 May 2021].reliability: 3.5/5 - Author has a PhD in politic, from a science school newsletter article.
Rodgers III, W. and Freeman, R., 2019. How Robots Are Beginning to Affect Workers and Their Wages. [online] The Century Foundation. Available at: <https://tcf.org/content/report/robots-beginning-affect-workers-wages/> [Accessed 27 May 2021].reliability: 4/5 - from a proper company that researches topics like these, American based information and isn't based on covid.
Romei, V., 2020. Pandemic boosts automation and robotics. [online] Ft.com. Available at: <https://www.ft.com/content/358f6454-e9fd-47f3-a4b7-5f844668817f> [Accessed 1 June 2021].reliability: 4.5/5 - comes from a large newspaper company, uses statistics from many different sources, author has experience with statistics and economics.
Thomas, Z., 2020. Coronavirus: Will Covid-19 speed up the use of robots to replace human workers?. [online] BBC News. Available at: <https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-52340651> [Accessed 1 June 2021].reliability: 3.5/5 - uses information from multiple sources, author is a technology reporter, large company.